

Throughout the life of the organism, populations of adult stem cells serve as an internal repair system that generates replacements for cells that are lost through normal wear and tear, injury, or disease. Those reprogramed stem cells are called induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). In 2006, researchers identified conditions that would allow some mature human adult cells to be reprogrammed into an embryonic stem cell-like state. Previous work with mouse embryos led to the development of a method in 1998 to derive stem cells from the inner cell mass of preimplantation human embryos and to grow human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) in the laboratory. The inner cell mass will ultimately develop into the specialized cell types, tissues, and organs of the entire body of the organism. The trophectodermal cells contribute to the placenta. Adult stem cells are found in a tissue or organ and can differentiate to yield the specialized cell types of that tissue or organ.Įarly mammalian embryos at the blastocyst stage contain two types of cells – cells of the inner cell mass, and cells of the trophectoderm. Pluripotent stem cells have the ability to differentiate into all of the cells of the adult body.

There are several main categories: the “pluripotent” stem cells (embryonic stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells) and nonembryonic or somatic stem cells (commonly called “adult” stem cells).
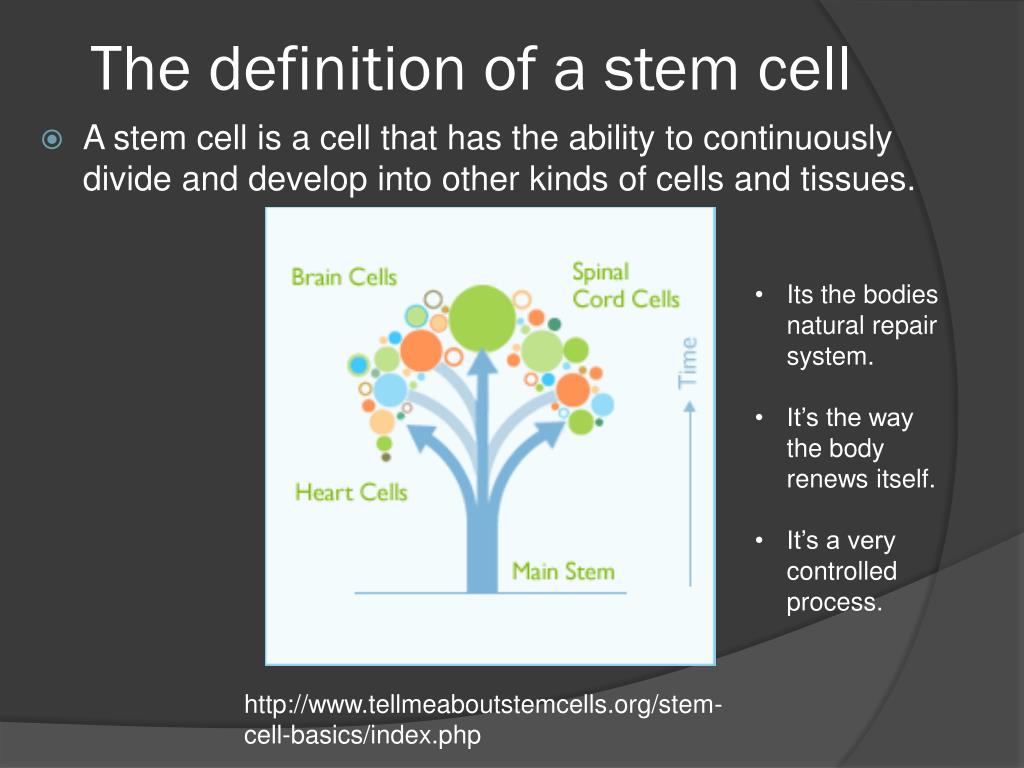
Researchers study many different types of stem cells. They can develop into many different cell types in the body during early life and growth. Stem cells have the remarkable potential to renew themselves. Introduction: What are stem cells, and why are they important?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
